When we talk about building AI data centers, east-west GPU fabrics often steal the spotlight. But there’s another traffic path that’s just as critical: north-south connectivity. In today’s AI environments, how your data center ingests data and delivers results at scale can make or break your AI strategy.
Why north-south traffic now matters most for AI at scale
AI is no longer a siloed project tucked away in an isolated cluster. Enterprises are rapidly evolving to deliver AI as a shared service, pulling in massive volumes of data from external sources and serving results to users, applications, and downstream systems. This AI-driven traffic generates the bursty, high-bandwidth north-south flows that characterize modern AI environments:
- Ingesting and preprocessing huge datasets from object stores, data lakes, or streaming platforms
- Loading and checkpointing large models from high-performance storage
- Querying vector databases and feature stores to provide context for retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) and agentic workflows
- Serving real-time inference to thousands of concurrent users or microservices
AI workloads amplify traditional north-south challenges; often they arrive in unpredictable bursts, can move terabytes in minutes, and are highly sensitive to latency and jitter. Any stall leaves expensive GPUs idle and elongates job completion times, drives up costs, and diminishes returns on AI investments.
Understanding the AI cluster: a multi-network architecture
It’s easy to imagine an AI cluster as a single, monolithic network. In reality, it’s a composition of several interconnected networks that must work together predictably:
- Front-end network connects users, applications, and services to the AI cluster.
- Storage network provides high-throughput storage access.
- Back-end compute network carries GPU-to-GPU traffic for computation.
- Out-of-band management network for baseboard management controller (BMC), host management, and control-plane access.
- Data center fabric, including border/edge, ties the cluster into the rest of the environment and the internet.
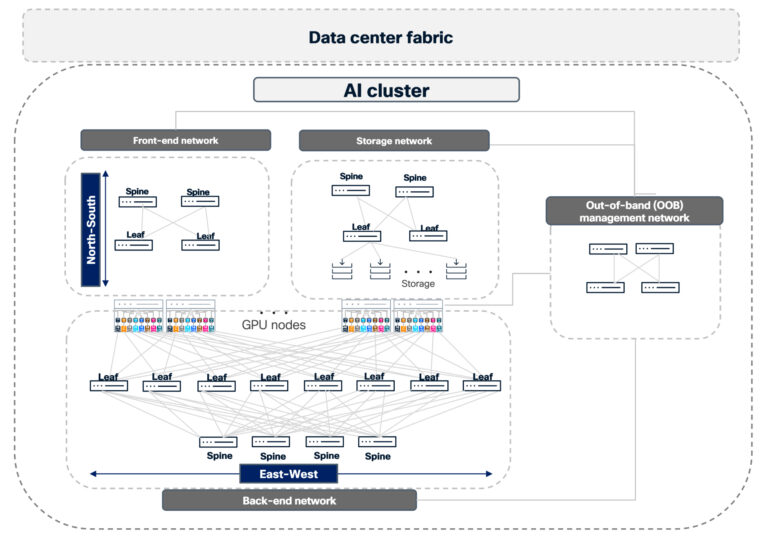

Peak performance isn’t just about bandwidth, it’s about how well your fabric handles congestion, failures, and operational complexity across all of these planes as AI demand grows.
How north-south connectivity impacts GPU efficiency
Modern AI relies on continuous, real-time interactions between GPU clusters and the outside world. For example:
- Fetching live data from external application programming interfaces (APIs) or enterprise sources and partner systems
- High-speed loading of training sets and model checkpoints from converged storage fabrics
- Performing dynamic contextual lookups from vector databases and search indices for RAG and agent-based workflows
- Serving high-QPS inference for user-facing applications and internal services
These patterns generate:
- Bursty, unpredictable loads: Batch/distributed inference jobs can suddenly consume significant bandwidth, stressing uplinks and core links.
- Tight latency and jitter budgets: Even short-lived congestion or microbursts can cause head-of-line blocking and slow down GPU pipelines.
- Risk of static hot spots: Traditional static equal-cost multi-path (ECMP) hashing cannot adapt to changing link utilization, leading to congested paths and underutilized capacity elsewhere.
To keep your GPUs fully utilized, your north-south network must be congestion-aware, resilient, and easy to operate at scale.
Simplifying AI infrastructure with converged front-end and storage networks
Many leading AI deployments are converging front-end and storage traffic onto a unified, high-performance Ethernet fabric distinct from the east-west compute network. This architectural approach is driven by both performance requirements and operational efficiency—allowing customers to reuse optics and cabling while leveraging existing Clos fabric investments, significantly reducing cost and cabling complexity.
This converged north-south fabric:
- Delivers high-performance storage access over 400G/800G leaf-spine architectures
- Carries host management and control-plane traffic from management nodes to compute and storage nodes
- Connects to border leaf or core switches for external connectivity and tenant ingress/egress
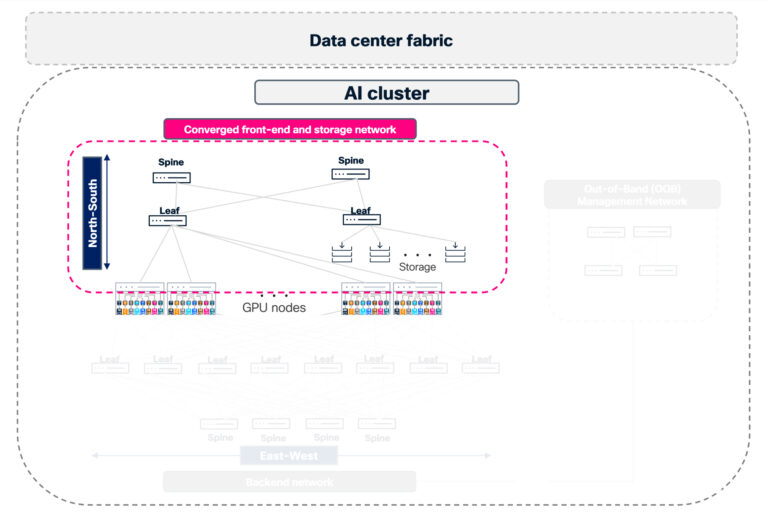

Cisco N9000 switches running Cisco NX-OS are purpose-built for these unified fabrics, delivering both the scale and throughput required by modern AI front-end and storage networks. By combining predictable, heavy storage traffic with lighter, latency-sensitive front-end application flows, you can maximize your fabric’s efficiency when it’s properly engineered.
Optimizing AI traffic with Cisco Silicon One and Cisco NX-OS
Managing north-south AI traffic isn’t just about merging inference, storage, and training workloads on one network but can also be about addressing the challenges of converging storage networks connected to different endpoints. It’s about optimizing for each traffic type to minimize latency and avoid performance dips during congestion.
In modern AI infrastructure, different workloads demand different treatment:
- Inference traffic requires low, predictable latency.
- Training traffic needs maximum throughput.
- Storage traffic can have different patterns between high-performance storage, standard storage, and shared storage.
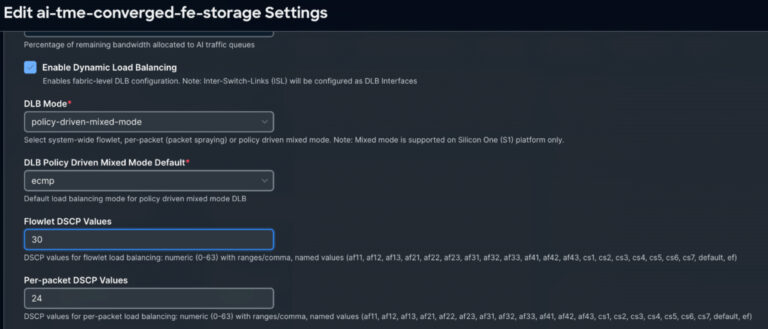
While the back-end fabric primarily handles lossless remote direct memory access (RDMA) traffic, the converged front-end and storage fabric carries a mix of traffic types. In the absence of quality of service (QoS) and effective load-balancing mechanisms, sudden bursts of management or user data can lead to packet loss, which is catastrophic for the strict lossless ROCEv2 requirements. That’s why Cisco Silicon One and Cisco NX-OS work in tandem, delivering dynamic load balancing (DLB) that operates in both flowlet and per-packet modes, all orchestrated through sophisticated policy control.
Our approach uses Cisco Silicon One application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) paired with Cisco NX-OS intelligence to provide policy-driven, traffic-aware load balancing that adapts in real time. This includes the following:
- Per-packet DLB: When endpoints (such as SuperNICs) can handle out-of-order delivery, per-packet mode distributes individual packets across all available links in a DLB ECMP group. This maximizes link utilization and instantly relieves congestion hot spots—critical for bursty AI workloads.
- Flowlet-based DLB: For traffic requiring in-order delivery, flowlet-based DLB splits traffic at natural burst boundaries. Using real-time congestion and delay metrics measured by Cisco Silicon One, the system intelligently steers each burst to the least-utilized ECMP path—maintaining flow integrity while optimizing network resources.
- Policy-driven preferential treatment: Quality of service (QoS) policies override default behavior using match criteria such as differentiated services code point (DSCP) markings or access control lists (ACLs). This enables selective per-packet load balancing for specific high-priority or congestion-sensitive flows, ensuring each traffic type receives optimal handling.
- Coexistence with traditional ECMP: DLB traffic leverages dynamic, telemetry-driven selection while non-DLB flows continue using traditional ECMP. This allows incremental adoption and targeted optimization without requiring a forklift upgrade of your entire infrastructure.
This simultaneous mixed-mode approach is particularly useful for north-south flows such as storage, checkpointing, and database access, where congestion awareness and even utilization directly translate into better GPU efficiency.
Scaling AI operations using Cisco Nexus One with Nexus Dashboard
Cisco Nexus One is a unified solution that delivers network intelligence from silicon to software—operationalized through Cisco Nexus Dashboard on-premises and cloud-managed Cisco Hyperfabric. It provides the intelligence required to operate trusted, future-ready fabrics at scale with assured performance.
As AI clusters and network fabrics grow, operational simplicity becomes mission critical. With Cisco Nexus Dashboard, you gain a unified operational layer for seamless provisioning, monitoring, and troubleshooting across your entire multi-fabric environment.
In an AI data center, this enables a unified experience, simplified automation, and AI job observability. Using Cisco Nexus Dashboard, operators can manage configurations and policies for AI clusters and other fabrics from a single control point, significantly reducing deployment and change-management overhead.
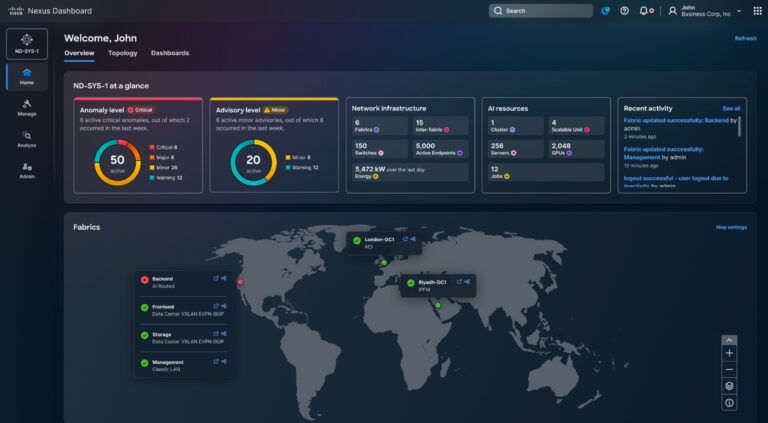

Nexus Dashboard simplifies automation by providing templates and policy-driven workflows to roll out best-practice explicit congestion notification (ECN), priority flow control (PFC), and load-balancing configurations across fabrics, significantly reducing manual effort.

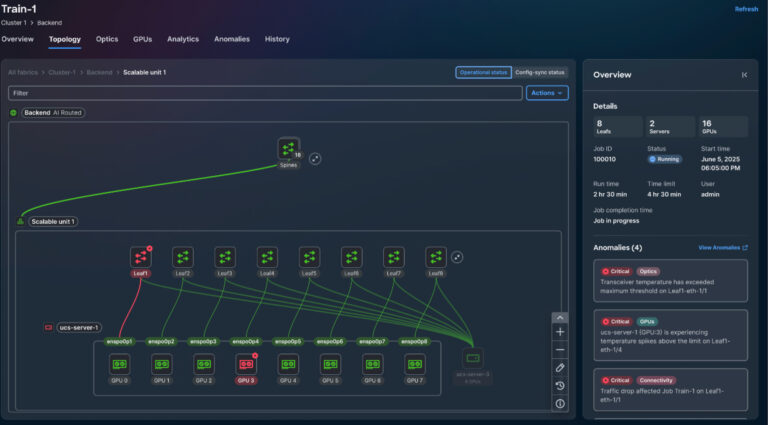
Using Cisco Nexus Dashboard, you gain end-to-end visibility into AI workloads across the full stack, enabling real-time monitoring of networks, NICs, GPUs, and distributed compute nodes.

Accelerating AI deployment with Cisco Validated Designs
Cisco Validated Designs (CVDs) and Cisco reference architectures provide prescriptive, proven blueprints for building converged north-south fabrics that are AI-ready, removing guesswork and speeding deployment.
North–south connectivity in enterprise AI—key takeaways:
- North-south performance is now on the critical path for enterprise AI; ignoring it can negate investments in high-end GPUs.
- Converged front-end and storage fabrics built on high-density 400G/800G-capable Cisco N9000 switches provide scalable, efficient access to data and services.
- Cisco NX-OS policy-based load balancing mixed-mode is a powerful capability for handling unpredictable traffic in an AI cluster while preserving performance.
- Cisco Nexus Dashboard centralizes operations, visibility, and diagnostics across fabrics, which is essential when many AI workloads share the same infrastructure.
- Cisco Nexus One simplifies AI network operations from silicon to operating model; enables scalable data center fabrics; and delivers job-aware, network-to-GPU visibility for seamless telemetry correlation across networks.
- Cisco Validated architectures and reference designs offer proven patterns for secure, automated, and high-throughput north-south connectivity tailored to AI clusters.
Future-proofing your AI strategy with a resilient network foundation
In this new paradigm, north-south networks are making a comeback, emerging as the decisive factor in your AI journey. Winning with AI isn’t just about deploying the fastest GPUs; it’s about building a north-south network that can keep pace with modern business demands. With Cisco Silicon One, NX-OS, and Nexus Dashboard, you gain a resilient, intelligent, and high-throughput foundation that connects your data to users and applications at the speed your organization requires, unlocking the full power of your AI investments.

