Securing specific compute capacity can be challenging, especially during high-traffic (and high-pressure) periods. Data engineers and platform administrators are all too familiar with the frustration of insufficient capacity, or “stockout”, errors that occur when a cluster launch fails because a cloud provider cannot fulfill a request for a specific instance type.
Whether it’s:
AWS_INSUFFICIENT_INSTANCE_CAPACITY_FAILURECLOUD_PROVIDER_RESOURCE_STOCKOUTon Azure, orGCP_INSUFFICIENT_CAPACITY,
These errors disrupt critical workloads, especially during business-critical periods when uptime matters most.
What Are Flexible Node Types?
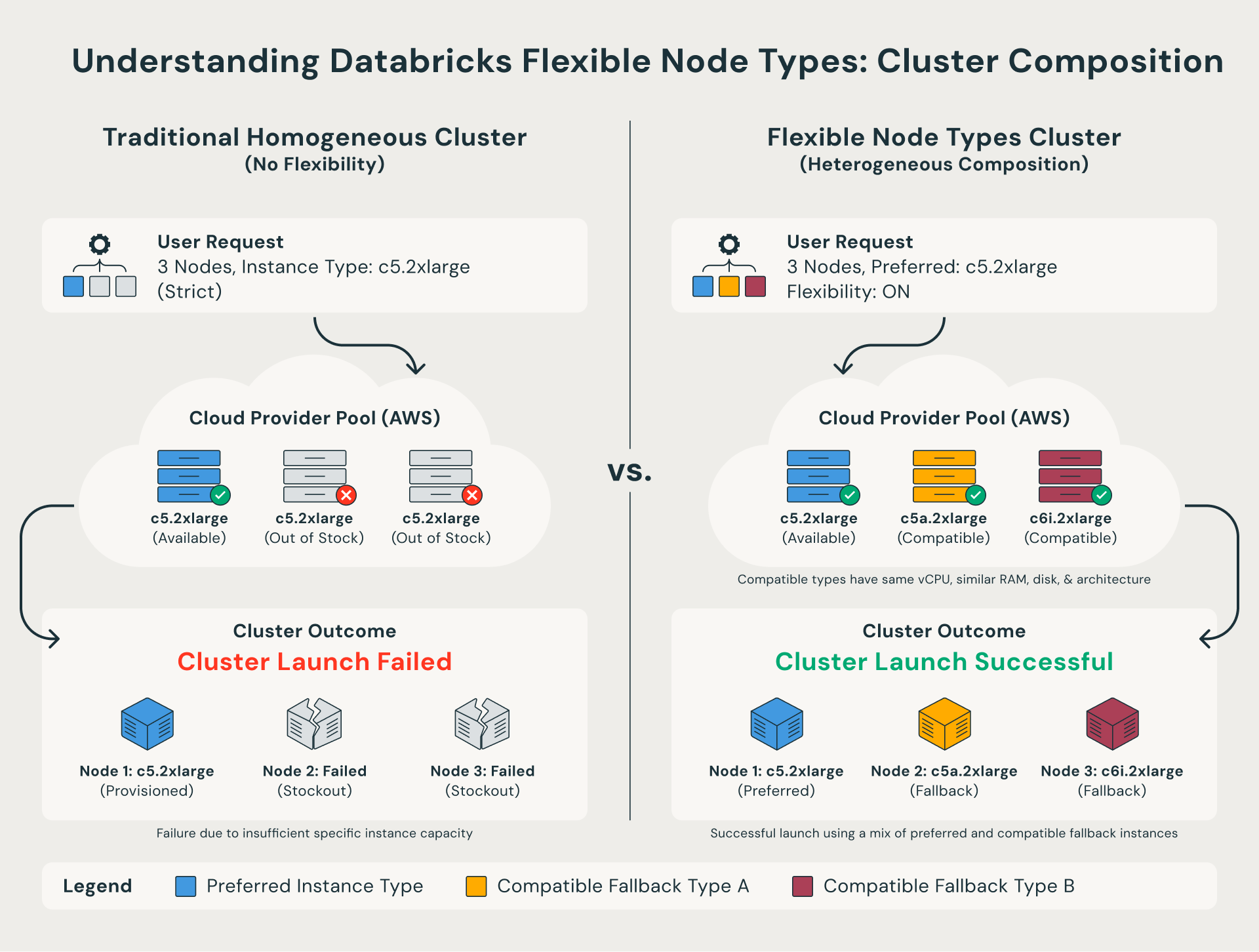
Traditionally, Databricks clusters required every node to be the exact instance type specified in your configuration. If that specific type were unavailable, the cluster launch would fail.
Flexible node types remove this constraint. When a preferred instance type isn’t available, Databricks automatically falls back to a compatible alternative that shares the same compute shape. In other words, the cluster successfully launches using a mix of similar instance types instead of failing outright.
For teams that need tighter control, they can also define a custom fallback list through the API, including which instance types to try and in what order.
Key Benefits
Fewer failed cluster launches during peak demand
Flexible node types reduce both the frequency and severity of capacity-related failures. When a cloud provider cannot fulfill the preferred instance type, Databricks automatically falls back to compatible alternatives, allowing clusters to launch rather than erroring out.
Optimized Spot Instance Usage
For clusters configured with Spot-with-fallback, flexible node types attempt to acquire Spot capacity across the full fallback list before reverting to On-Demand instances. This increases the portion of the cluster running on Spot, helping lower compute costs while still prioritizing successful launches.
Clear visibility and precise control
Teams can inspect exactly which node types are acquired using the node_timeline system table. Additionally, a custom fallback order can be defined via the API, allowing precise control over cost and performance behavior.
Quick Start
Workspace admins can easily enable the feature in admin settings (Docs: AWS, Azure, GCP). From there, the feature applies immediately to all new cluster launches. Long-running clusters will adopt the feature on their next restart, and future job clusters created for existing jobs will automatically utilize the feature.
Custom fallback lists can be configured through the API, independent of the workspace setting.
Additional details
Please see the documentation for further details on configuring flexible node types with instance pools, billing, node type quotas, and selective enablement / disablement (Docs: AWS, Azure, GCP).
Flexible Node Types are designed to make your data platform more resilient and cost-effective. Administrators can 1-click enable this feature today in the workspace admin settings following the instructions in the documentation.

